This article covers the different ways you can embed charts and dashboards - all using the free, Open Source Edition of Metabase. If you’re looking for info on how to embed the entire Metabase app in your own application with the Enterprise Edition, check out this article.
We’ll go over:
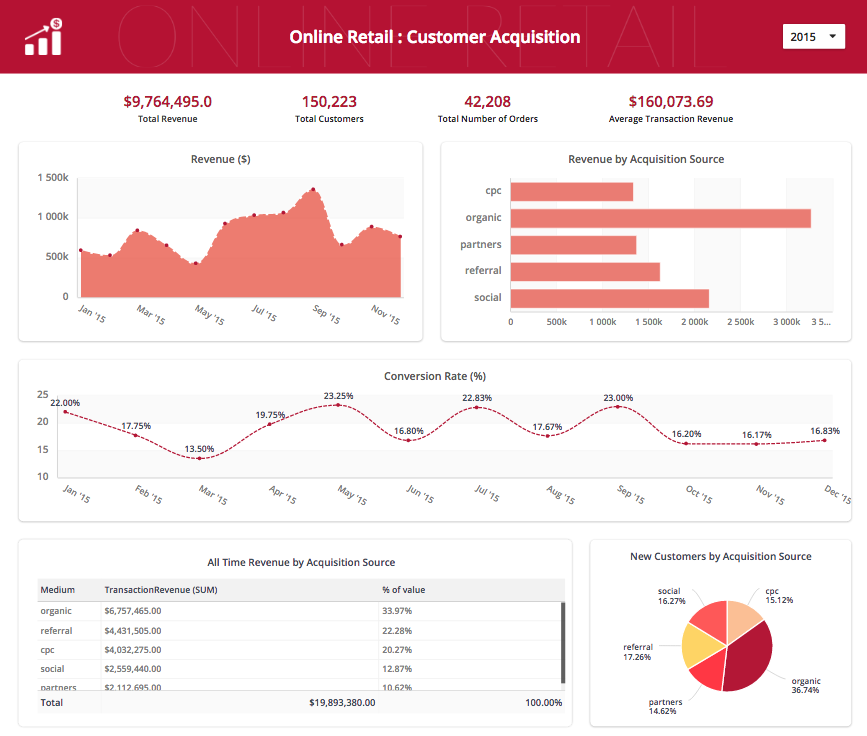
Building a dashboard summarizing the Northwind Database. SQL and Metabase. In this project, I built a dashboard using open source service Metabase summarizing the Northwind Database. It is a sample database that is shipped along with Microsoft Access. The data is about “Northwind Traders”, a fictional company. Now we use this data to create a few charts on our dashboard. Connect Metabase to our SQLite Database. Navigate to the settings icon on the top right and click Admin. Select Databases; delete the sample dataset; and click Add Database; Note: the path to the file is relative to the volume mounted into our docker container in part 1 of this post.
- Public links
- Public embeds
- Embedding questions and dashboards in your application (AKA signed embeds).
Public links and embeds
For quick sharing of questions and dashboards, you can simply send a public link, or drop an iframe in your website (or in anything that renders HTML). This is a great way for sharing charts and dashboards on the fly.
Enable public sharing
In order to share links to questions and dashboards, an admin must enable public sharing for your Metabase. Until sharing is enabled, Metabase won’t give us the public URL or iframe HTML.
To enable sharing, we’ll click on the gears icon in the main navigation bar, then select Admin. Once in the Admin panel, under the Settings tab’s left sidebar, we’ll select Public Sharing, and toggle on Enable public sharing.
All of our shared dashboards and questions will be listed here (once we start sharing them), and we’ll be able to disable the link as well.
Sharing options
Let’s say we want to share a dashboard, like the one in figure X. We’ll click on the sharing icon (the arrow pointing up and to the right), and select the Sharing and embedding option.
This will bring up our Sharing options:
Public links
A public link is the easiest way to share a dashboard. Public links aren’t even embeds; they’re just links to a single question or dashboard, though these public items are a little different than their original versions.
These public links will include a Powered by Metabase footer, which you can remove with Enterprise embedding. The charts will also have their action menus disabled, and we won’t be able to customize click behavior on a dashboard.
If we have a default filter value set, Metabase will apply that filter to the question or dashboard. People will be able to change the filter, so we can’t rely on filters to restrict which data people can see. To lock (or hide) a filter, we’ll need to use a signed embed.
We can also format the URL to assign a value to a filter, or hide the filter altogether - though keep in mind that the recipient can simply edit the URL. See our documentation to learn more about assigning values to filters or hiding them via the URL.
While these public links are hard to guess, anyone with that link could view our dashboard, so it’s not the best solution for sharing sensitive data. Still, we can quickly share a public link to a dashboard (with a customer, for example), then disable it once they’ve seen it. If we share the dashboard again, Metabase will generate a new link (so we don’t need to worry about access to the old link). If you accidentally share a link, you can disable it at any time; just toggle the sharing to off. Admins can view and disable all public links from the Admin panel.
Public embeds
We can embed a question or dashboard in our website using an iframe (an inline frame). It’s as simple as copying and pasting code from your Metabase and dropping it into the source code of a webpage. We can even use it with no-code website builders - anywhere we can drop in HTML. For example, you can embed a dashboard in a blog to help tell a story with data, or simply fill the whole page with a dashboard.
Here’s an iframe to display a dashboard:
An iframe creates another, nested browser window inside the current browser window. The iframe window points to its own URL, and presents the response from that address - in this case, the chart or dashboard we want to present. Like the public link, the chart will feature the Powered by Metabase footer.
We can adjust the width and height to suit our chart or dashboard. If we’re embedding a dashboard and the iframe isn’t wide enough to accommodate the dashboards layout, Metabase will stack the questions in the order they appear, from left to right, on the dashboard.
Enable embedding in other applications
Here’s where we start to get serious. If we want to restrict who can see our chart or dashboard, or lock a filter, we’ll need to use a signed embed. This feature is separate from the public sharing options, and accessible only to admins. We’ll also have to enable the Embedding in other Applications setting before it’ll work. In the Admin panel -> Settings tab, along the left sidebar, we’ll click on Embedding in other Applications, and toggle Enabled.
Let’s return to the dashboard we want to share. With embedding enabled, we’ll get a secret key.
To set up a signed embed, we’ll need to insert some code on our server to sign JSON Web Tokens (JWT) for our users. Metabase will generate code for some languages: Clojure, Python, Ruby, and Javascript (Node.js), but you should be able to translate that code for servers written in other languages as well.
Before we hit Publish, let’s review some of our options.
Hide or lock parameters to restrict what data is shown
If our question or dashboard has a filter, we can disable the filter, or lock parameters to set a fixed filter value.
Let’s say we want to show someone a dashboard, but we only want to let them see orders in the Gadget category.
In our example, the parameters set the filter on the dashboard. Here we set the Category filter to Gadget.
Here’s some example code for a server written in Clojure:
This code will use the secret key that Metabase gives us to sign the JSON Web Token (JWT) (our users will not - and should not - see the secret key).
Here’s how it will go down.
- In Metabase, we Publish the dashboard we want to embed in our application.
- We insert the iframe into a page of our application.
- We place the code to sign JSON web tokens in our server.
- Our user logs into our application.
- The user requests a page in our application with the embedded dashboard.
- When the server handles the request for that page, it will sign the user’s token and insert that token as the iframe’s source URL.
- When the page loads, the page requests the dashboard from our Metabase instance using the signed token.
- The dashboard loads in an iframe in our application with the paramaters and expiration set by our application server.
If the token is not signed, or if it’s altered in any way, the dashboard won’t load.
In the payload map, we can specify when the signed JWT will expire (in the code above, the token expires after 10 minutes).
The :params field is where we can lock a parameter to set a default, fixed filter on your dashboard or question. For example, we could create a dashboard with a filter for a user ID, then - on our server - programmatically insert a user’s ID as parameter. The signed token will lock the filter to that ID, so any user who sees that dashboard will only see data that’s been filtered by their ID.
Full app embedding
If you want to unlock the full potential of Metabase when embedding, which would allow people to drill through the data, or send them to custom destinations (like other dashboards, or external URLS), you’ll need full app embedding. To learn more, see Deliver analytics to your customers and Embed Metabase in your app to deliver multi-tenant, self-serving analytics.
Further reading
With its most recent IPO that took the whole Wall Street by storm, everyone in the data market space is talking about Snowflake - a cloud-based data warehouse-as-a-service.

As companies are eagerly switching from traditional server-based data warehouses to modern server-less ones (as described in detail by Lars Kamp in his letter to his investors), it's very likely that your company is looking at adopting Snowflake and revamping the complementary data stack.
In response to this movement, as a data analyst/engineer, you set out to find the most compatible BI and reporting tools for this data source.
Although Snowflake has kindly listed out all BI tools that it can inter-operate with, it is not enough for us to simply decide which one fits our company's demand for data.
This blog will give you a detailed comparison of the top 5 Snowflake BI & reporting tools, which hopefully will give you some pointers to choosing the most suitable one for your current data stack.
- Holistics
- PowerBI
- Looker
- Tableau
- Metabase
Holistics
Holistics is a self-service BI tool that lets data analysts model and transforms data in Snowflake and many other SQL data warehouses. Then, non-technical users can run their own analysis to insights without having to rely on the analysts any more.
Holistics is best-known for its data modeling capability, which can help analysts create a single source of truth where you can apply business logic to your own data and make sure it is accurate, maintainable, and re-usable.
You can learn how to connect Holistics to Snowflake in their detailed guide here.
Pricing
Holistics generously offers a free plan after your 14-day trial expires, which does not charge you based on the number of users, but on the number of query runs. That means, if you are a bootstrapped startup with limited budget, Holistics is the right tool for you. It will only start charging as your company and its analytics need scales up.
Holistics starting price of $200/month is impressively affordable when compared to almost all competitors on the market, especially when its features are equally powerful and plentiful. Even if your company scales up with more analysts joining the data team, you will not need to worry about cost per additional head count.
Pros
- Allow you to query the Snowflake database using customizable SQL queries and get fast results with its cache layer
- Materialized views of query results are stored back to your own SQL database, for immediate access and fast visualizations and reports.
- Automated scheduling of reports and dashboard with the latest data in Snowflake, sent directly to your email inbox.
- Advanced SQL Editor: Version History, Autocomplete, SQL Snippet, Highlighting, Auto-formatting, Query History, Custom Advanced Logic...
- Drag-and-drop interface for business users to explore data and generate reports to answer ad-hoc questions.
- Competitive pay-as-you-go pricing model, which only scales as your company scales.
Cons
- Though powerful, Holistics is a fairly new tool to the market. A lot of advanced features are still on their roadmap.
- Holistics has not supported Git-integration and version control, which is preferable to a lot of advanced analysts.
- Dashboards are not as interactive as other competitors'. Currently Holistics only supports drill-down by date and drill-through to another dashboard.
PowerBI
Metabase Download
PowerBI is quite well-known in the BI industry, especially for enterprises that adopt the Microsoft ecosystem. It supports an impressive number of data sources, giving companies the power to centralize their data in one place.
PowerBI has a user-friendly interface with amazing data visualizations capabilities, ranging from simple dashboards that analyze eCommerce metrics to highly complicated ones like the NFL Football analysis one below.
Connecting PowerBI to Snowflake is fairly simple. You can follow the instructions here.
Pricing
PowerBI pricing is also attractive for small-scale companies with small data teams. If you're an individual and only need PowerBI on your local computer to do analysis, then you can download the desktop version for free. However, if you want to use more Power BI services and publish your reports on the cloud, you can take the Power BI Cloud service solution for $9.99 per user per month.
Please note that if your company is concerned about security and on-premise deployment, the price goes up considerably at $4,995 per month, with an annual subscription.
Pros
- Support hundreds of data sources, from cloud service like Snowflake to offline files like Excel
- Powerful data visualization capabilities. Besides the basic visualization types, PowerBI allows advanced users to choose from a market place of custom visuals or create their own using well-known Javascript libraries
- Frequent updates and innovations. Follow PowerBI's blog and you will see the team is really active in pushing new features and changes.
- PowerBI has an active community of power users and employees who are willing to deep dive into your use case to help you out.
Cons
- PowerBI has a steep learning curve. Data analysts must learn DAX (Data Analysis Expression) language to fully leverage PowerBI's power, which is complicated and rigid sometimes.
- Limited data delivery capability. If you want to view a PowerBI report, you must have PowerBI desktop installed or have PowerBI Report Server already setup. This is difficult for Mac users since PowerBI can only be installed on Windows devices.
Looker
Recently joined as a part of Google Cloud Platform, Looker is a powerful BI tool that provides an innovative approach for real-time data exploration and analytics.
Looker has powerful dashboard capabilities that can cover most data discovery use cases. However, unlike Power BI, it requires a full semantic model for storing all your business logic and metrics without having to add multiple versions of a slightly different metric to your database tables. That means you cannot just take Looker, point it at a database, and get your visualizations in minutes. It requires an upfront definition using their own language LookML, which will take a considerable amount of time to master.
To connect Looker to Snowflake, follow the instructions here.
Pricing
Looker does not publicly release its pricing information because they will customize for each company. From my conversations with a few Looker users, the price could range from $3000 - $5000 per month for 10 users with an annual subscription. As I mentioned above, Looker is designed for companies with mature and dedicated data teams that are willing to adopt a completely new modeling language and spend time setting up Looker to fit their whole data stack.
Pros
- Looker runs entirely in-browser, so there’s no need for desktop install and it's better for collaboration and data delivery between internal and external users
- Looker operates entirely on the data in your database. That means that you’re operating directly on your full dataset and getting all the horsepower of your database, whether that be an MPP like Vertica, Redshift, Bigquery; a SQL-on-Hadoop setup like Impala or Spark; or a standard RDBMS like MySQL or Postgres
- Automated reporting - Looker allows you to schedule emails for daily/weekly/monthly reports or send alerts if there are anomalies in data.
- Looker has GitHub integration, so you can see every change made to the modeling layer and combine the work of multiple developers seamlessly
Metabase Training
Cons
- Looker has a steep learning curve when it comes to adopting a new language (LookML) & the model-view approach for the end-users. You definitely need to have an internal team that is dedicated to just setting it up and getting the rest of the people on board.
- Being locked in the platform. LookML takes over most of the work of preparing tables for visualization. Moving from Looker to another visualization tool will require additional work to migrate everything that has been defined by LookML.
- Although Looker provides a large library of custom charts, it can be very difficult to customize the visualizations to your exact need.
Tableau
Tableau is most famous for its unparalleled capabilities of visualizing information. The application’s data visualizing quality is superior to what Tableau software competitors offer. If you want to create complicated dashboards with seamless interactivity, Tableau is definitely the must-have tool.
To connect Tableau to Snowflake, read more here.
Metabase Sample Dashboard Template
Pricing
Tableau pricing is fairly complicated and is charged both based on your use-case and number of team members. Moreover, Tableau also charges based on the roles of users, with a Creator costing $70/month, an Explorer $35, and a Viewer $12. Since this number is dependent on your business, you really should plan ahead and prepare for an upsurge of additional cost if you decide to purchase Tableau.
Pros
- Great visualization capabilities: a large library of charts and highly interactive dashboards
- Tableau's friendly interface allows data analysts of all experience levels to quickly begin producing compelling and useful analysis and visualizations.
- Tableau handily deals with millions of rows of data, from various data sources, including spreadsheets and SQL databases. This allows users to integrate disparate data sources that may have been difficult to connect otherwise.
Cons
- Like PowerBI, Tableau cannot handle too big a dataset. It will get very slow. If you import data from multiple sources and the data is huge, it sometimes tends to lag crash.
- Lack of BI capabilities. Tableau lacks functionality required for a full-fledged business intelligence tool, such as large-scale reporting, the building of data tables and static layouts.
- Tableau Desktop lacks the basic functionality of cleaning and prepping the data to be imported in Tableau Desktop. This is one of the major features which it lacks, you need additional support from Tableau to get these things added.
Metabase
Not as equally popular as Holistics, PowerBI, or Tableau, Metabase is an open-source tool designed for non-technical users to provide big data insights and visualizations.
Metabase is best for businesses of all sizes that want to deploy either cloud-based or on-premise versions. You can use Metabase for KPI monitoring, database management, bug tracking, record filtering, debugging, and query builder.
Metabase does support connecting to Snowflake, but you might want to take into consideration a few things.
Pricing
Free
Pros
- Metabase is free and open-source. Metabase is licensed under GPLv3 with source code available on GitHub, which you can use to deploy on your own server and maintain on your own.
- Metabase is lightweight to install.
- The UI is simple and friendly so it takes little training to use the tool effectively.
Cons
- Metabase only works well with a single SQL data source. If you have data from multiple sources, chance is you might want to find another tool because it does not allow you to join table data.
- Despite having the desktop version, Metabase sometimes gets very buggy and slow to render the results.
- Contrary to Tableau, Metabase has limitations regarding customizing how the charts look.
- Because it is self-hosted, companies must handle the administration issues and app updates on their own, which might take a lot of time and effort.

Any of the five tools mentioned above will work well with Snowflake, but not all of them are suitable for your company.
Sometimes, the most powerful, feature-rich tool might not be the best choice, as it comes with too high a price or too steep a learning curve.
Therefore, if you're an analyst tasked with finding such tool, a good advice is to involve a lot of your colleagues and end-users to use the product intensively during the free trials. You will then understand the real bottlenecks of each tool and make the wisest choice.
If you need a little more pointer to choose the right tool, you might want to check out Chapter 4 in The Analytics Setup Guidebook which will discuss in detail how you can navigate the Business Intelligence tool space.
